The Challenge
The ability to drive revenue, increase margins, and reduce cost to serve, while still engaging, retaining, and growing customers, is the fundamental measure of success for organizations. The definition of ‘customer’ varies across industries as consumers, businesses, students, clients, donors, or constituents; however, the fundamental ability to attract, engage, and retain relationships is universal. The missing ingredient for many organizations is shared understanding of who the customer is and how their activities impact customer perceptions and future sales success.
Many organizations have repeatedly attempted and failed to effectively deploy and fully utilize CRM systems and processes to measure and predict sales and service effectiveness. The common factor is a focus on the creation of forecasts based on current presses, resulting in unreliable data and poor adoption.
By leveraging solutions for forecasting alone, organizations miss the opportunity to align processes and data with sales strategies – driven by the voice of the customer. This is a result of leveraging the CRM as a system of accountability against weak forecasts, instead of a strategic system for enabling sales strategies. This lack of sales enablement reduces adoption and creates inefficiencies, while leadership confidence in sales data declines. Organizations grapple with every aspect of sales performance, including sales structures and incentives, tools, data, and reporting while customer needs and interactions remain largely unaddressed.
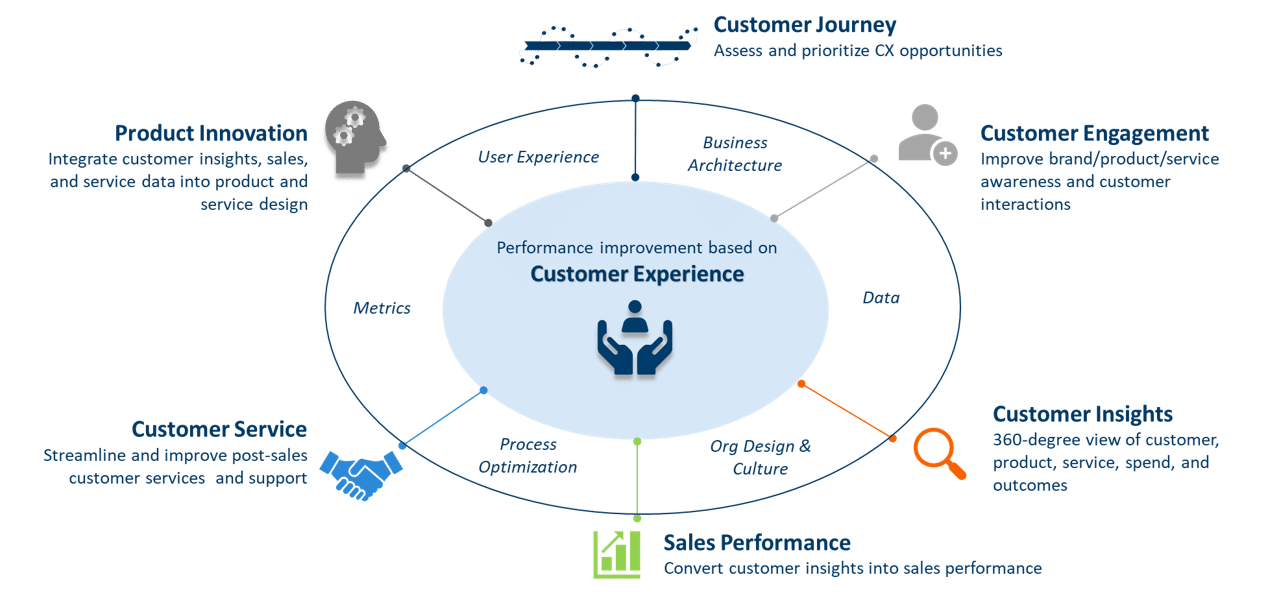
The Customer Experience (CX) Framework
Traditional CRM planning and delivery are based on technology project management processes. Whether agile or waterfall, requirements are commonly based on fragmented internal business needs rather than an outcome-based strategy. The Customer Experience Framework provides the foundation for Sales, Marketing, Technology, and Services to align on customer experiences to deliver measurable business outcomes, increasing the ROI of CRM and customer impacting technology investments.

Centering on Customer Experience
Internal departments may have misaligned interest and priorities when it comes to desired outcomes. This is largely a result of differing priorities and incentives. The IT department wants to contain cost, reduce complexity, and ensure supportability. Marketing wants to measure campaign impact on sales. Sales leaders wants to ensure visibility of the opportunity pipeline. Business leadership wants forecasts. Internal alignment is gained when everyone agrees on a common external focal point that results in measurable business impact. The CX Framework engages all stakeholders and realigns focus on value creation through improvements to customer experience outcomes, measured by sales performance.
Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping originates in the concepts of empathy mapping within Design Thinking and has roots in “Moments of Truth” as coined by author, Jan Carlzon, former president of Scandinavian Airlines. Carltzon described a business Moment of Truth as, “Any time a customer comes into contact with a business, however remote, they have an opportunity to form an impression.” An impression is an opportunity to create lasting impact and exceed expectations and value.

Establishing the vision and opportunity for Customer Experience can begin by bringing key customer impacting roles together to participate in a customer journey mapping workshop. During the full day workshop, participants map customer interactions based on the customer’s perspective, the customer’s wants and needs, and opportunities to improve a moment of truth. Post workshop surveys reflect 98% of participants find customer journey mapping workshops valuable, even though it typically requires a full day out of very busy, often global schedules.
Customer journey maps identify new priorities, reveal gaps in business architecture, and shift technology and data requirements. The maps identify ‘moment of truth’ improvements that will require changes to processes, organizational design, culture, and technology. Moving forward, customer journey maps allow organizations to proactively architect new moments for truth for your customers.
Customer Engagement
Customer journey maps reveal opportunities to establish or improve customer engagement. Customer engagement begins with awareness of your brand, services, and products and is reinforced or weakened by impressions during sales, contracting, services, and loyalty efforts. The impression from a point of engagement, whether digital or physical, become the new point of measurement for success. Connecting each stage of customer engagement drives growth by creating a well-designed experience that exceeds customer expectations.
Customer Insights
Customer data may only consist of measuring service incidents, online engagement, marketing responses, and sales opportunities. This represents a small fraction of the customer impressions. Once all customer engagement points are better identified and understood, organizations can begin gathering and connecting meaningful customer insights along the entire customer journey.
Data-driven customer insights provide an ongoing measurement of shifts in customer expectations, becoming a driver in strategic planning for sales success. Many organizations today do not consider metrics such as ease of contracting, speed of customer issue resolution, or consistency in customer engagement processes as key business metrics; however, these cross-functional measures, along with many others, could be critical to improving customer interactions and impressions.
Sales Performance
Commercial organizations are fundamentally measured by sales performance, not customer experience alone. It is essential to tie experiences and insights back to sales and product improvements, enabling ongoing performance improvement. Executing on CX strategies may require changes to organizational structures, incentives, and sales processes while aligning product design, service design, and internal operations back to sales performance. This alignment should identify business opportunities, such as new product or service development, cross-selling, upselling, product bundling, or ROI-driven marketing campaigns. An effective CX strategy should also assess expected sales impact from ‘internal’ initiatives that can impact sales in unexpected ways.
Customer Service
Integrating ongoing customer touchpoints after the initial sale is essential to enabling future sales. Customer Service focuses on all post sales customer engagement activities. Customer empathy and engagement improvements are continuously identified and re-integrated into improvement initiatives. Opportunities are then assessed for impact to future sales and service strategies.
Metrics
Creating cross-functional, transparent metrics that inform the entire customer journey strategy ensures ongoing internal alignment and performance gains. New marketing, sales, and services dashboards extend beyond financial measures and pipelines to customer service performance, customer sentiment analysis, internal sales, marketing and product collaboration metrics.

Product Innovation
Customer Experience leaders convert customer insights into internal changes, performance outcomes, and innovation. Customer expectations change over time. Delivering the same tried-and-true product or service design, sales, and delivery model may work for a few legacy industries, but the age of digital often drives customers to ever higher levels of expectations for value, convenience, and performance. High-value customer engagement improvements must integrate into product and service design and/or research and development activities on a continuous basis.
CX Building Blocks
Establishing CX as the primary driver requires a careful look at the current state of CX building blocks including:
Organizational Culture
- Awareness and commitment to Customer Experience strategy
- History of cross-functional collaboration on customer outcomes
- Clear owners of customer impacting functions and interfaces
- Degree of focus on data transparency
Processes
- Documented and aligned customer engagement processes
- Consistent use and measurement of marketing, sales, contacting, and delivery interactions with customers to improve outcomes
- Process for identifying and addressing customer experience insights across functions
Technology & Data
- Identify customer engagement systems
- Identify customer data source systems
- Standard tools and governed data for customer impacting processes
- External brand listening and social media monitoring
- Digital customer feedback and engagement mechanisms
- User experience strategy driven by customer experience strategy
Customer Experience Metrics
- Customer sentiment analysis
- Customer loyalty metrics
- Use of Net Promotor Score
- Customer feedback and measurement
Operational Metrics
- Marketing ROI
- Product Revenue
- Sales Pipeline & Velocity
- Call Center Response Time
- Accounts Receivable
User Champion & Adoption
- Executive Sponsor(s) – Executives with a strong stake in CX outcomes. They own the priority and champion the message and progress to employees and customers/the market.
- Product Owners – Functional Owner responsible for strategy, roadmap and messaging of customer facing services and products.
- Change Agents – Leaders and direct managers who advocate for change. They must be involved and consistently communicating expectations.
- Change Network – A group of team members responsible for cross-organizational customer experience improvement; committed to advocating project success.
- Change Leadership – Lead for building and managing adoption strategies. Plugging in external change resources support to manage and create plans and messages aides in success.
Integrating Customer Experience into CRM Deployments
Driving customer experience strategy, data, processes, and alignment may require unique customer experience process, data, and change management roles working directly with executive sponsors and leaders to provide project management and building or improving internal capabilities. This is real-world of exercise of rebuilding the plane while in flight.

Customer Experience Roles
Customer experience roles focus on establishing the CX strategy, identifying data requirements, re-designing processes, and ensuring effecting change management.
CX Advisor
- Support CX / CRM strategy development, execution, and alignment
- Ensure CX related project commitments and risks are effectively managed
- Support alignment between business program functions, change/comms, and system requirements
CX Process Design Engineer
- Document processes, assess change impacts, and lead redesign efforts
- Work with program leadership and IT to translate processes to technical criteria
Change Management and Communications
- Develop program messaging and communication strategy
- Develop process champions within internal organizations
- Document and validate process and tool training requirements
CX Data Analyst
- Establish customer, product, and service data strategy
- Design and build CX performance dashboards for Marketing, Sales, Product, or Services Teams
- Create CX metrics, measurement, and reporting
Success and Ongoing Outcomes
The Customer Experience Framework aligns CRM priorities, enables cross-functional alignment, ensures effective adoption of tools and processes, and builds a lasting customer experience improvement capability that can drive future strategy and sales performance.

CRM, Marketing, Sales and Support strategies must begin by looking at the customer. Serving your customers’ needs and wants provides organizations a common purpose and framework for performance. What does the customer want from your organization? What data confirms how well you are delivering on those needs? If leads and sales forecast reports are the only requirements guiding CRM journey, sales strategy, or marketing plans – your organization may miss an incredible opportunity to center planning, performance measurement and outcomes on customer outcomes that can drive future innovation and sales.